Enabling username aliasing
In some scenarios, a particular user wants to print a job but his/her username has been changed for various reasons and it is reflected in PaperCut now as a different username. Examples of why the username has changed include:
-
Two networks/domains/servers have different naming conventions, e.g. for user John Smith, one network uses the convention "j.smith" while the other uses "jsmith".
-
For some policy reasons, the format of usernames has changed and you want to allow forgetful users to log in with their previous username.
-
Print jobs are coming from an ERP or mainframe system where usernames are different.
-
In some organizations, users log in with employee numbers.
-
Print jobs coming from some software packages might use the "application username" and not the user's network username used by PaperCut. This can occur in some SAP configurations.
-
Unix has strict requirements for usernames, (IEEE Std 1003.1–2001), where the only valid characters are letters, digits, underscores, full stops, at-signs, dashes (but not start with a dash) and having $ at the end. So when printing on a Unix server, it can sanitize the username, such as converting an apostrophe into an underscore, and then recording in PaperCut as a different user when one really wants it to be the same user.
To work around this problem PaperCut allows users to have an alias for their username. The username alias is applied at the following levels:
-
User login to the web interface, client popup authenticationPopup authentication involves matching the source IP address of the print job with the user confirmed to be operating from the popup client IP address. Authentication is provided by the PaperCut NG client software in the form of a popup dialog requesting a username and password. To print with popup authentication the client software must be running on the workstations or laptops., or Release StationPrint Release Stations place a print job on hold and allow users to release it when required. Often a Release Station is a dedicated PC terminal located next to the printers, however, Release Stations can take other forms such as a web browser based interface. Some common examples where Release Stations can be used include secure printing, approved printing, and authentication. In a secure printing environment jobs are only printed when the user arrives at the print area and confirms his or her identity. This ensures the user is there to collect the job and other users can't "accidentally" collect the document. In some organizations it may be appropriate to hold jobs until they are approved by selected individuals. A good example would be a teacher approving printing on an expensive color printer. Hold/Release queues can be used as a form of authentication in an unauthenticated environment. Users must authenticate prior to releasing their jobs allowing PaperCut NG to confirm their identity. login.
-
Print jobs arriving in the print queues under the alias.
Enable username aliasing
-
Select Options > Advanced.
The Advanced page is displayed.
-
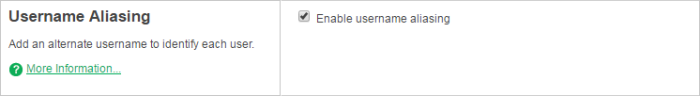
In the Username Aliasing area, select the Enable username aliasing check box.
-
Click Apply.
Once username aliasing is enabled, Username alias is displayed on the User Details page.
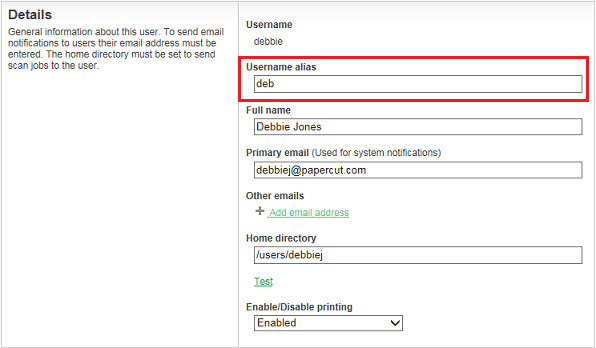
You can import this information from Active Directory or LDAPThe Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is a directory service protocol that runs on a layer above the TCP/IP stack. It provides a mechanism used to connect to, search, and modify Internet directories. The LDAP directory service is based on a client-server model. during an overnight sync. Once username aliasing is enabled, an option to enter an AD/LDAP field name is displayed under Options > User/Group sync. You can choose any valid Active Directory user field to import this information. For example: employeeNumber, employeeID, otherLoginWorkstations.
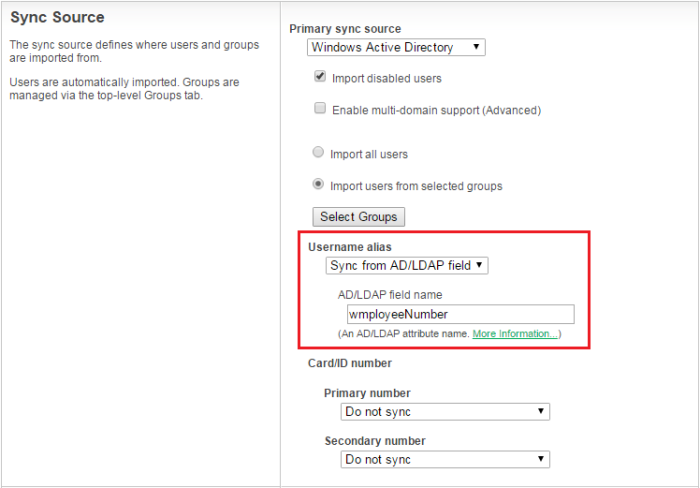
Once this is set, information from this Active Directory field is imported every night as username aliases. For more information on user group synchronization see Synchronizing user and group details.
